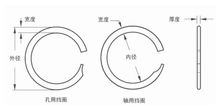
Characteristics and structure of Constant Section Rings
Constant Section Rings (CSRs) are also known as the Equal Section Rings, because the cross-section is equal and there is no protruding part of the traditional stamped ring. The CSRs have similarities with the spiral retaining rings in terms of production and use characteristics, both of which are made by flattening steel wire and winding it. After heat treatment and surface treatment, they have good elasticity and toughness. The CSRs are divided into two types: shaft and hole, with a variety of end options available.
Features of Constant Section Rings
The Constant Section Rings has the following characteristics:
☉ Equal cross-section and uniform stress distribution reduce stress concentration
The inner and outer circles are smooth and complete, without interfering with the mating parts
No burrs on the inner and outer diameters, easy to disassemble
☉ Little scrap material is generated during the production process, saving materials
☉ No need to make molds, by changing the thickness of the material, it can be easily made into light, medium and heavy load types
The production cycle is short, and a wide range of materials can be selected, including spring steel, stainless steel, copper, and other metal materials, which can be easily produced.
Application of Constant Section Rings
The application of earless retainer rings is similar to traditional C-type retainer rings, and is widely used in hydraulic component assembly, valves, instruments, various lock core components, needle roller bearings, pulleys, connectors, quick connectors, and other mechanical assemblies.
Constant Section Rings material
The Constant Section Rings can be made of various materials, such as spring steel, stainless steel, copper, and other metal materials, which can be easily produced. Currently, the commonly used spiral stop ring materials on the market are carbon spring steel, alloy spring steel 65Mn, stainless steel 304 (commonly used in the United States as 302), 316, 17-7PH, and in some cases, beryllium bronze alloy and high temperature alloy materials.